HybridCLR Source Code Structure and Debugging
HybridCLR Module Introduction
HybridCLR implements the following functionality:
- C++ implemented DLL parsing library
- Metadata registration. Since il2cpp is static AOT, the original code doesn't support dynamic registration, so we made minor modifications (a few hundred lines)
- Instruction set transformation. Converts original IL instructions to more efficient register instructions
- Register interpreter. Implements an efficient interpreter.
In terms of directory structure, these correspond to:
- HybridCLR's own source code
- interpreter - interpreter module
- metadata - metadata parsing and registration module
- transform - instruction set transformation module
- Minor modifications to il2cpp source code. HybridCLR's modifications to il2cpp source code are mainly to support dynamic metadata registration. Most places just insert hook handling without modifying the original implementation. For example:
const char* il2cpp::vm::GlobalMetadata::GetStringFromIndex(StringIndex index)
{
// ==={{ hybridclr
if (hybridclr::metadata::IsInterpreterIndex(index))
{
return hybridclr::metadata::MetadataModule::GetStringFromEncodeIndex(index);
}
// ===}} hybridclr
IL2CPP_ASSERT(index <= s_GlobalMetadataHeader->stringCount);
const char* strings = ((const char*)s_GlobalMetadata + s_GlobalMetadataHeader->stringOffset) + index;
return strings;
}
Transform Implementation Overview
The core code is in the HiTransform::Transform function in hybridclr/transform/Transform.cpp.
Very similar to conventional instruction tree analysis. It consists of several parts:
- BasicBlock division. Splits original IL instructions into multiple BasicBlocks, each containing no jump functions. This efficiently avoids accidental instruction merging across jump blocks
- Simulates execution of all logical branches, including jump and exception branches, converting each IL instruction to corresponding register instructions.
- Instruction optimization (TODO). Expected to start development in next month's version. Most instructions are expected to achieve 100-300% performance improvement.
Interpreter Implementation Overview
The core code is in the Interpreter::Execute function in hybridclr/interpreter/Interpreter_Execute.cpp.
Quite straightforward, just a huge switch statement that interprets and executes instructions.
Debugging
HybridCLR interpreter's core work includes two parts:
- Instruction set transformation. Converts stack-based IL instructions to register-based versions. In the HiTransform::Transform function in HybridCLR/transform/transform.cpp.
- Interpretive execution of register instructions. In the Interpreter::Execute function in HybridCLR/interpreter/interpreter_Execute.cpp.
By setting breakpoints in these two functions, you can easily trace the entire flow from IL function transformation to execution step by step.
Creating Win, Mac Standalone Debug Project
Project Settingsconfiguration- Change
C++ Compiler Configurationto Debug
- Change
- Check "Create VisualStudio Solution" in
Building Settings
After building, a debuggable project is generated. For more information, refer to Unity's official documentation
Creating Android Debug Project
Project Settingsconfiguration- Change
C++ Compiler Configurationto Debug
- Change
- Check
Export ProjectinBuilding Settings - After building, open the project with Android Studio.
- Assuming the build output path is build_android, in Android Studio select Build->Make Module 'build_android.unityLibrary', compile unityLibrary, and wait for compilation to complete
- Select
Run->Edit Configurations...and configure as shown in the image below.
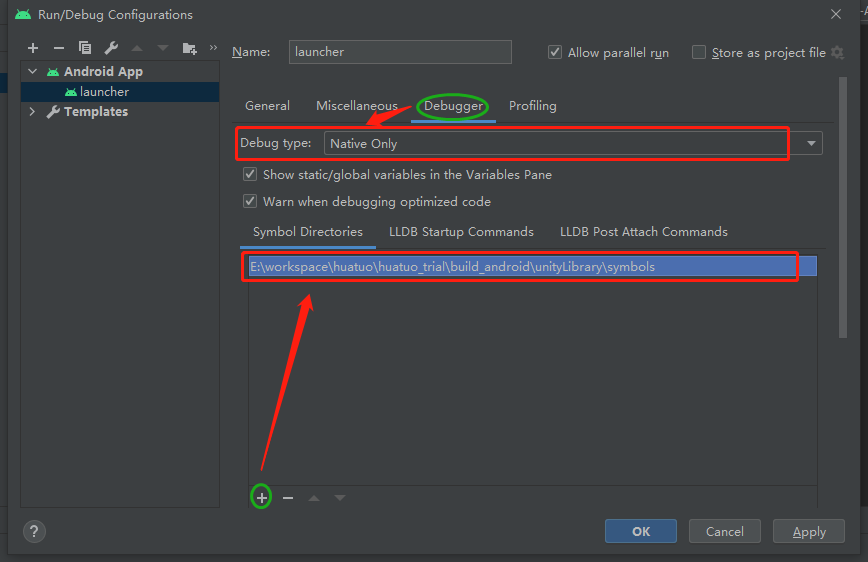
- Debug normally.
Creating iOS Debug Project
You must use com.code-philosophy.hybridclr v3.2.0 or higher to directly debug source code. Lower versions use independently compiled release version libil2cpp.a, which cannot be debugged.
Project Settingsconfiguration- Change
C++ Compiler Configurationto Debug
- Change
- Click
Buildto generate Xcode project - Debug within the Xcode project