Execution Performance
Although HybridCLR also uses interpretation execution, both theoretical principles and real device testing data show that HybridCLR has dramatically improved performance (multiple times or even dozens of times) compared to popular hot update solutions like Lua and ILRuntime.
Test Report
HybridCLR is currently the highest-performing CLR interpreter implementation and the most performant among all hot update solutions, with comprehensive performance exceeding other solutions by more than an order of magnitude.
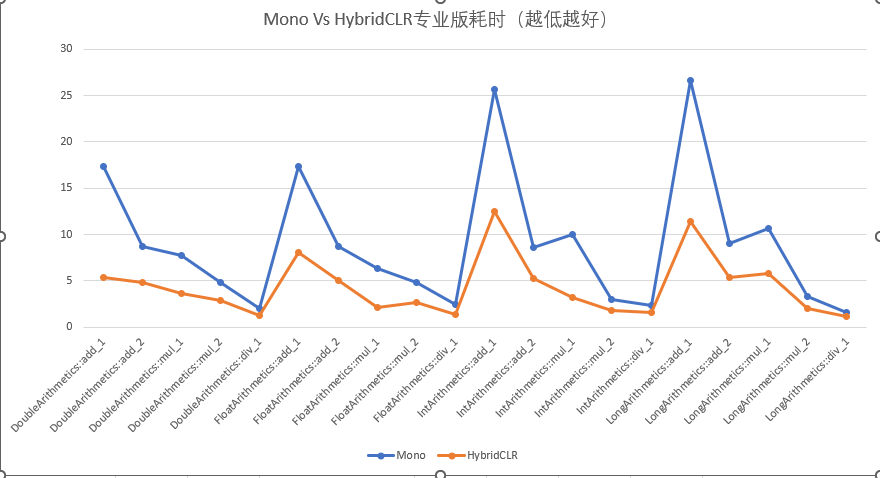
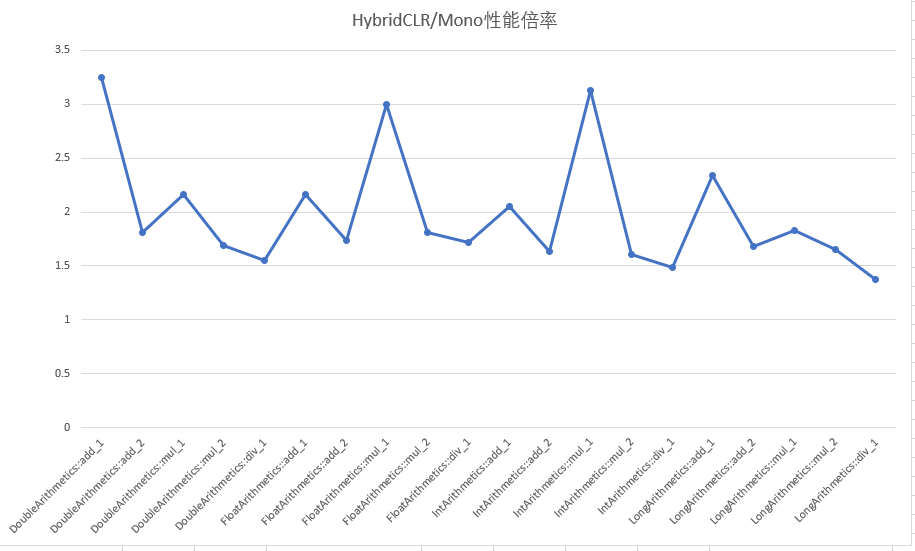
The comprehensive performance of HybridCLR's commercial version significantly outperforms Mono's mint implementation, with numerical computation instruction performance ranging from 140%-330% of Mono's performance.
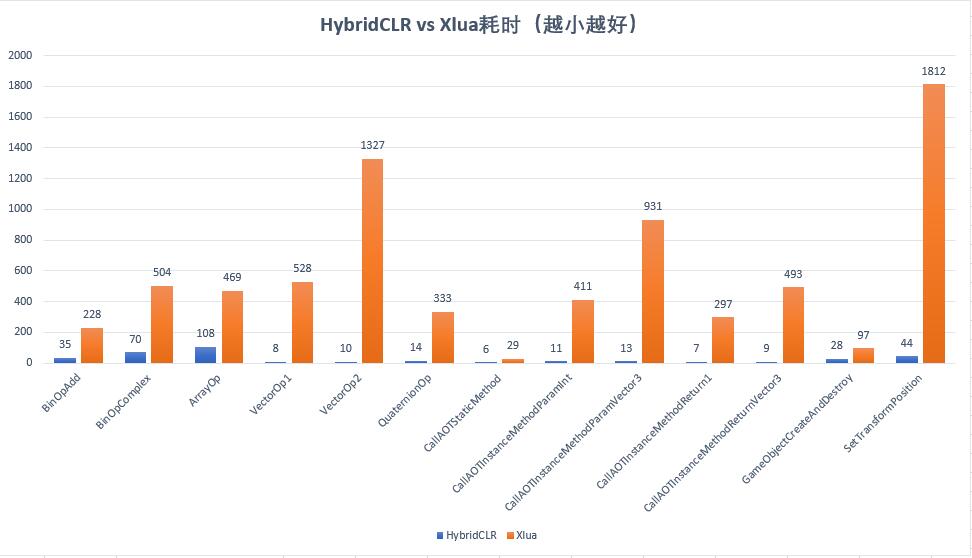
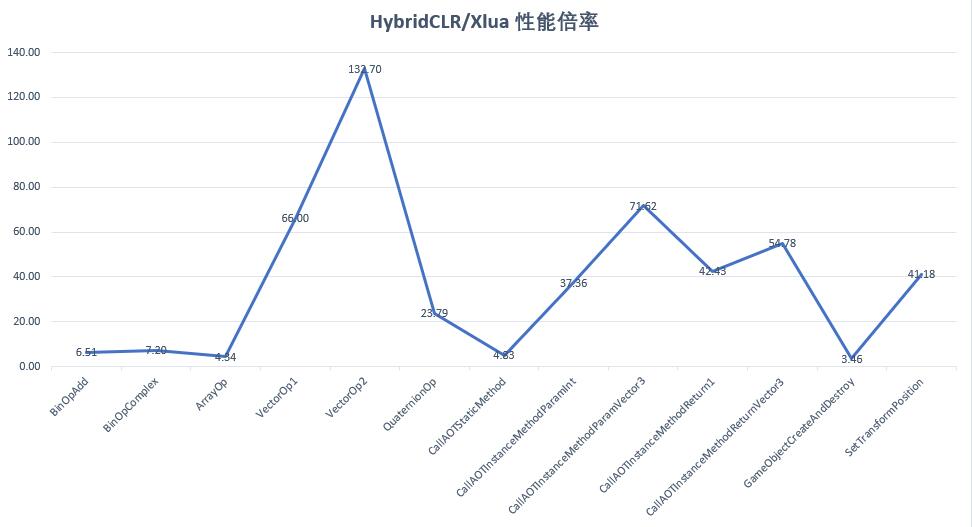
HybridCLR's commercial version completely dominates the xlua solution, with numerical computation instruction performance at 651%-720% of xlua's performance, and being dozens or even hundreds of times faster than xlua in other aspects.
The community version of HybridCLR has a noticeable gap with AOT only in numerical computation, while other aspects show minimal differences. Therefore, for most projects, the overall game performance is not significantly different from a fully native version.
The commercial version of HybridCLR dramatically optimizes numerical computation performance, achieving 280%-735% of the community version's performance. Developers with strict performance requirements can contact us for commercial services.
The following is a test report from OnePlus 9R ArmV8 real device testing, with test code provided in the appendix.
HybridCLR Commercial Version Time vs Mono Time
HybridCLR Commercial Version/Mono Performance Ratio
HybridCLR Commercial Version Time vs xlua Time
HybridCLR Commercial Version/xlua Performance Ratio
AOT Time vs Commercial Version Time vs Community Version Time (Lower is Better)
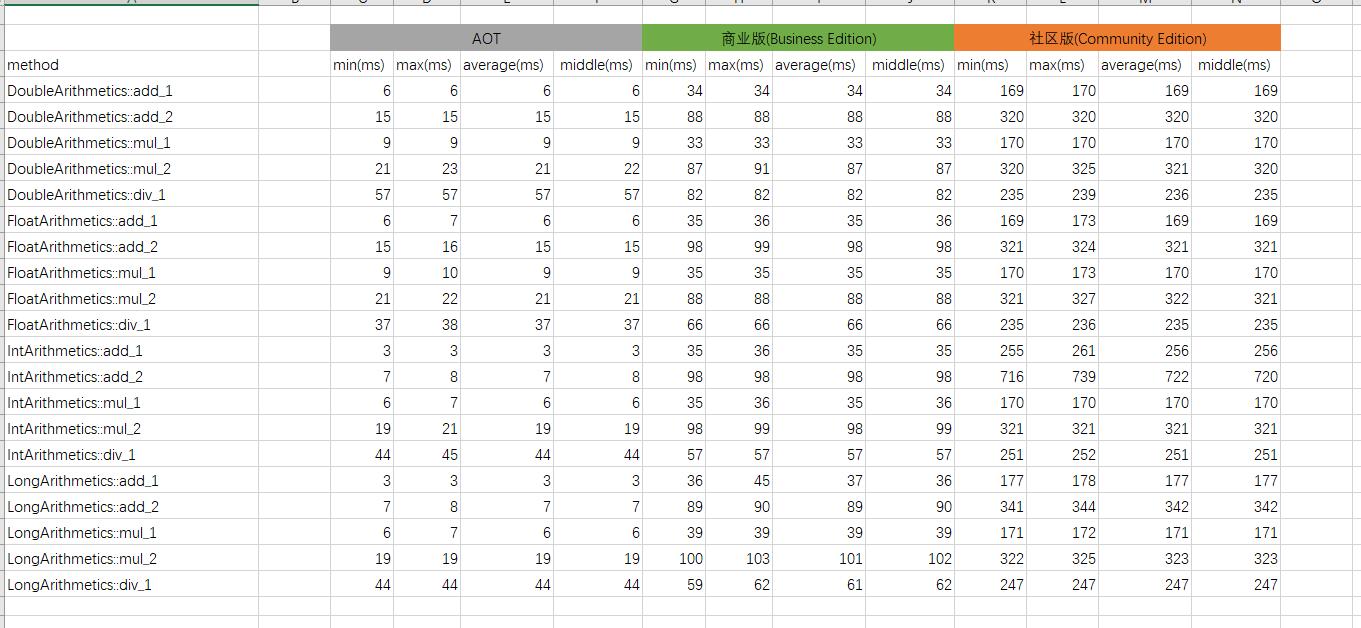
Commercial Version Time/AOT Time vs Community Version Time/AOT Time (Lower is Better)
AOT version performance is 4.1 - 90 times that of the community version, and 1.30 - 12.9 times that of the commercial version.
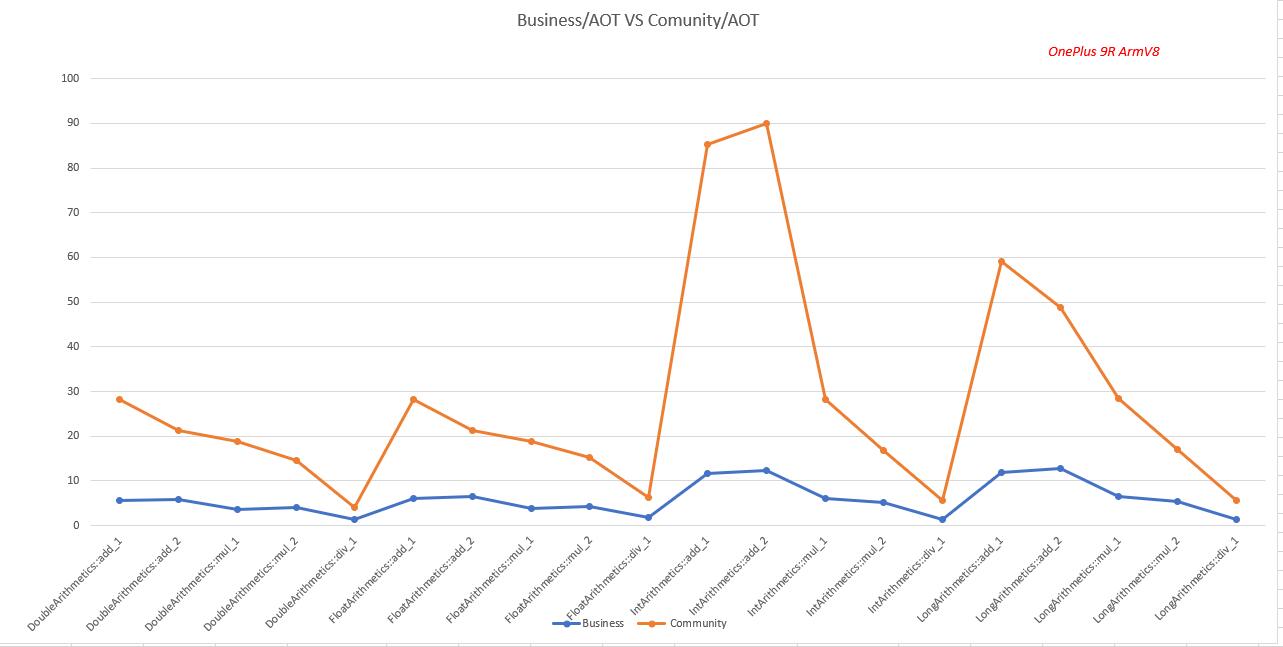
Commercial Version Performance/Community Version Performance (Higher is Better)
Commercial version performance is 2.87-7.35 times that of the community version.
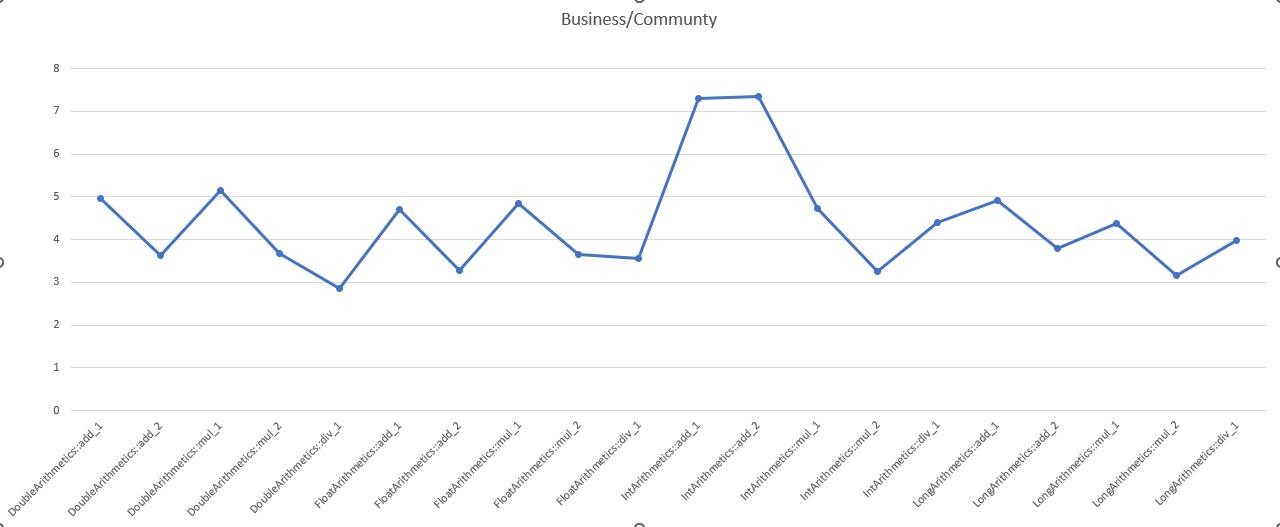
Commercial Version Time/AOT Version Time (Lower is Better)
AOT version performance is 1.30 - 12.9 times that of the commercial version.
Principles
Since HybridCLR is implemented in C++ and directly integrates seamlessly with the il2cpp runtime, it can directly access low-level runtime data and various interfaces. Compared to ILRuntime and xlua, it eliminates additional costs at the C# layer, significantly reducing interaction costs.
HybridCLR's excellent performance mainly comes from the following aspects:
Rewritten Streamlined and Efficient Metadata Parsing Library
We didn't use existing metadata parsing libraries but implemented a streamlined and efficient C++ metadata parsing library according to HybridCLR's requirements. Other C# hot update or hotfix solutions all use C# libraries like Cecil, resulting in huge differences in memory and loading efficiency!
Using Register Instruction Set
Original IL bytecode is a stack-based instruction set. HybridCLR converts it to a register instruction set, reducing stack maintenance overhead.
Direct Access to Data Stack and Execution Stack
Stack operations are the most common operations in CLI, with almost all instructions involving stack operations. Since the interpreter stack is self-maintained heap memory, CLI has limitations on struct pointer operations. If implementing an interpreter in C#, you cannot directly operate data types on the interpreter stack and must use various techniques to achieve this indirectly. HybridCLR, being implemented in C++, can operate directly.
Operating struct types has several to dozens of times improvement in efficiency compared to other interpreters.
Static Instruction Specialization
Some instructions like the add instruction are multi-functional instructions that decide the final operation based on the operand types on the current stack. HybridCLR designs add_i4, add_i8, add_r4, add_r8 - these 4 instructions. When translating instructions, it calculates the current stack data types and translates to corresponding specialized instructions. This saves runtime type judgment overhead and runtime data type maintenance overhead.
Pre-calculating Runtime Metadata that Needs to be Resolved
Some instructions like ldtoken and ldstr need to convert instruction data to actual runtime data at runtime. HybridCLR directly calculates the corresponding runtime data during translation and saves it to the converted instructions, greatly improving performance.
Simple and Efficient Implementation of Object Member Access Instructions
Object member access instructions like v.x = b; are very common. Solutions like ILRuntime and xlua, due to C# language limitations, must operate through wrap function calls. HybridCLR, being implemented in C++, can directly access object memory data. By pre-calculating field offsets in objects, it can complete this access operation directly with *(int32_t*)(obj + offset) = b;.
This provides dozens of times efficiency improvement compared to other hot update solutions.
Direct Support for Reference and Pointer Operations Without Indirect Methods
Due to CLI specification limitations, references in C# can only be placed on the managed stack, not stored on the interpreter stack (because it's heap memory). To handle code like ref int a = ref b; a = 5;, very complex techniques must be used to indirectly maintain this reference. HybridCLR, implemented in C++, can directly save and operate on this data.
Efficiency is greatly improved compared to other hot update solutions.
Unified Metadata, More Efficient Object Creation, and Smaller Memory Usage
Due to unified metadata, il2cpp::vm::Object::New can be called directly to create objects, with efficiency very close to native and identical memory usage. In contrast, other hot update solutions use fake types with bloated objects and more complex object creation processes.
Efficiency is greatly improved compared to other hot update solutions.
Unified Metadata, Unified Function Call Methods, and No Additional PInvoke and ReversePInvoke Overhead
HybridCLR can directly call C++ functions translated from IL functions without any intermediate steps, while ILRuntime and xlua require various complex determinations and parameter conversions, plus additional overhead from PInvoke and ReversePInvoke between C#.
HybridCLR's interaction with il2cpp AOT parts is extremely lightweight and efficient. Performance issues are no longer a concern.
Additional Provision of Numerous Intrinsic Functions
For common operations like new Vector{2,3,4}, new string(), Nullable<T>.Value, etc., we directly provide corresponding instructions with runtime overhead even lower than AOT implementations.
This provides dozens of times efficiency improvement compared to other hot update solutions.
Strict Compliance with Specifications, No Unnecessary Additional Costs
Through careful design and optimization, HybridCLR avoids various unnecessary overhead. For example, GC during execution is completely identical to native il2cpp and mono.
Other Instruction Optimization Techniques
Other optimization techniques
Appendix: Test Case Code
Commercial Version vs xlua
- HybridCLR
- xlua
public class AOTForCallFunctions
{
public void Empty()
{
}
public int ReturnInt()
{
return 0;
}
public Vector3 ReturnVector3()
{
return default;
}
public void Func1(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e)
{
}
public void Func2(Vector3 a, Vector3 b, Vector3 c, Vector3 d)
{
}
}
public class BenchmarkTestCases
{
public const int kTestCount = 10000;
/// <summary>
/// Test simple numerical computation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 100)]
public int BinOpAdd(int n)
{
int a = 1;
int b = n;
int c = 2;
int d = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
/// <summary>
/// Test complex numerical computation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 100)]
public void BinOpComplex(int cnt)
{
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Test array operations
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 100)]
public int ArrayOp(int cnt)
{
var arr = new int[100];
int k = cnt % 100 + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
}
return arr[0];
}
/// <summary>
/// Test Vector3 operations
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public int VectorOp1(int cnt)
{
float m = 0f;
var v = Vector3.one;
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
}
return (int)m;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public int VectorOp2(int cnt)
{
Vector3 c = default;
var a = new Vector3(1, 2, 3);
var b = new Vector3(4, 5, 6);
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
}
return (int)c.x;
}
/// <summary>
/// Test Quaternion operations
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public int QuaternionOp(int cnt)
{
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
var q1 = Quaternion.Euler(i, i, i);
var q2 = Quaternion.Slerp(Quaternion.identity, q1, 0.5f);
var q3 = q2.normalized;
var q4 = Quaternion.Lerp(q3, q2, 0.5f);
}
return 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// Test calling AOT static member function
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public int CallAOTStaticMethod(int cnt)
{
float t = 0f;
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
t = Time.deltaTime;
}
return (int)t;
}
/// <summary>
/// Test calling AOT instance member function with int type parameter
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public int CallAOTInstanceMethodParamInt(int cnt)
{
var o = new AOTForCallFunctions();
int x = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o.Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
}
return x + 1;
}
/// <summary>
/// Test calling AOT instance member function with Vector3 type parameter
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public int CallAOTInstanceMethodParamVector3(int cnt)
{
var o = new AOTForCallFunctions();
Vector3 a = Vector3.one;
Vector3 b = Vector3.one;
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
o.Func2(a, b, a, b);
}
return 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// Test calling AOT instance member function, return type is int
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public int CallAOTInstanceMethodReturn1(int cnt)
{
var o = new AOTForCallFunctions();
int x = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
x = o.ReturnInt();
}
return x + 1;
}
/// <summary>
/// Test calling AOT instance member function, return type is Vector3
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public int CallAOTInstanceMethodReturnVector3(int cnt)
{
var o = new AOTForCallFunctions();
Vector3 x = default;
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
x = o.ReturnVector3();
}
return (int)x.x;
}
/// <summary>
/// Test GameObject creation and destruction operations
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount)]
public void GameObjectCreateAndDestroy(int cnt)
{
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
var go = new GameObject("t");
Object.Destroy(go);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Test Transform operations
/// </summary>
/// <param name="cnt"></param>
[Benchmark]
[Params(kTestCount * 10)]
public void SetTransformPosition(int cnt)
{
var go = new GameObject();
Vector3 v = Vector3.one;
for (var i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
}
Object.Destroy(go);
}
}
function BinOpAdd(cnt)
local a = 1;
local b = cnt;
local c = cnt;
local d = cnt;
for i = 1, cnt do
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
end
return a + b + c + d
end
function BinOpComplex(cnt)
local total = 0;
for i = 1, cnt do
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
total = total + i - (i - 2) * (i + 3);
end
return total
end
function ArrayOp(cnt)
local arr = {}
for i = 0, 100 do
arr[i] = 0
end
local k = cnt % 100 + 1;
for i = 1, cnt do
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
arr[k] = arr[k] + i;
end
return arr[0]
end
function VectorOp1(cnt)
local m = 0
local v = CS.UnityEngine.Vector3.one;
for i = 1, cnt do
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
m = v.sqrMagnitude;
end
return m;
end
function VectorOp2(cnt)
local c = CS.UnityEngine.Vector3.one;
local a = CS.UnityEngine.Vector3(1, 2, 3);
local b = CS.UnityEngine.Vector3(4, 5, 6);
for i = 1, cnt do
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
c = c + a;
c = c + b;
end
return c.x
end
local Quaternion = CS.UnityEngine.Quaternion
function QuaternionOp(cnt)
for i = 1, cnt do
local q1 = Quaternion.Euler(i, i, i);
local q2 = Quaternion.Slerp(Quaternion.identity, q1, 0.5);
local q3 = q2.normalized;
local q4 = Quaternion.Lerp(q3, q2, 0.5);
end
return 0;
end
function CallAOTStaticMethod(cnt)
local Time = CS.UnityEngine.Time
local t
for i = 1, cnt do
t = Time.deltaTime
end
return t
end
function CallAOTInstanceMethodParamInt(cnt)
local o = CS.AOTTypes.AOTForCallFunctions();
for i = 1, cnt do
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
o:Func1(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
end
end
function CallAOTInstanceMethodParamVector3(cnt)
local o = CS.AOTTypes.AOTForCallFunctions();
local a = CS.UnityEngine.Vector3.one;
local b = CS.UnityEngine.Vector3.one;
for i = 1, cnt do
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
o:Func2(a, b, a, b)
end
end
function CallAOTInstanceMethodReturn1(cnt)
local o = CS.AOTTypes.AOTForCallFunctions();
local x = 0;
for i = 1, cnt do
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
x = o:ReturnInt();
end
return x + 1;
end
function CallAOTInstanceMethodReturnVector3(cnt)
local o = CS.AOTTypes.AOTForCallFunctions();
local x
for i = 1, cnt do
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
x = o:ReturnVector3();
end
return x;
end
function GameObjectCreateAndDestroy(cnt)
for i = 1, cnt do
local go = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject("t")
CS.UnityEngine.Object.Destroy(go)
end
end
function SetTransformPosition(cnt)
local go = CS.UnityEngine.GameObject("t")
local v = CS.UnityEngine.Vector3.one;
for i = 1, cnt do
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
go.transform.position = v;
end
CS.UnityEngine.Object.Destroy(go)
end
AOT vs Community Edition vs Commercial Edition vs Mono
public class LongArithmetics
{
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public long add_1(long n)
{
long a = 1;
long b = n;
long c = 2;
long d = n;
for(long i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public long add_2(long n)
{
long a = 1;
long b = n;
long c = 2;
long d = n;
long e = 3;
for (long i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public long mul_1(long n)
{
long a = 1;
long b = n;
long c = 2;
long d = n;
for (long i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public long mul_2(long n)
{
long a = 1;
long b = n;
long c = 2;
long d = n;
long e = 3;
for (long i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public long div_1(long n)
{
long a = 1;
long b = n;
long c = 2;
long d = n;
for (long i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
a = a / n + 1;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
public class IntArithmetics
{
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public int add_1(int n)
{
int a = 1;
int b = n;
int c = 2;
int d = n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public int add_2(int n)
{
int a = 1;
int b = n;
int c = 2;
int d = n;
int e = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public int mul_1(int n)
{
int a = 1;
int b = n;
int c = 2;
int d = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public int mul_2(int n)
{
int a = 1;
int b = n;
int c = 2;
int d = n;
int e = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public int div_1(int n)
{
int a = 1;
int b = n;
int c = 2;
int d = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
a = a / n + 1;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
}
public class FloatArithmetics
{
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public float add_1(int n)
{
float a = 1;
float b = n;
float c = 2;
float d = n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public float add_2(int n)
{
float a = 1;
float b = n;
float c = 2;
float d = n;
float e = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public float mul_1(int n)
{
float a = 1;
float b = n;
float c = 2;
float d = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public float mul_2(int n)
{
float a = 1;
float b = n;
float c = 2;
float d = n;
float e = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public float div_1(int n)
{
float a = 1;
float b = n;
float c = 2;
float d = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
a = a / n + 1;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
}
public class DoubleArithmetics
{
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public double add_1(int n)
{
double a = 1;
double b = n;
double c = 2;
double d = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
a = b + c;
b = c + d;
c = d + a;
d = a + b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public double add_2(int n)
{
double a = 1;
double b = n;
double c = 2;
double d = n;
double e = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
a = b + c + d + e;
b = c + d + e + a;
c = d + e + a + b;
d = e + a + b + c;
e = a + b + c + d;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public double mul_1(int n)
{
double a = 1;
double b = n;
double c = 2;
double d = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
a = b * c;
b = c * d;
c = d * a;
d = a * b;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public double mul_2(int n)
{
double a = 1;
double b = n;
double c = 2;
double d = n;
double e = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
a = b * c * d * e;
b = c * d * e * a;
c = d * e * a * b;
d = e * a * b * c;
e = a * b * c * d;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
[Benchmark]
[Params(1000000)]
public double div_1(int n)
{
double a = 1;
double b = n;
double c = 2;
double d = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
b = c / a;
c = d / a;
d = b / a;
a = a / n + 1;
}
return a + b + c + d;
}
}